What are Cylinder Lenses?
Creating a Laser Line Generator | Creating Circular Beams | Selection Guide
Cylinder lenses are a type of lens that have differing radii in the X and Y axes, causing the lens to have a cylindrical or semi-cylindrical shape, and image magnification in only a single axis. Cylinder lenses are commonly used as laser line generators, or to adjust image height size or correct for astigmatism in imaging systems.
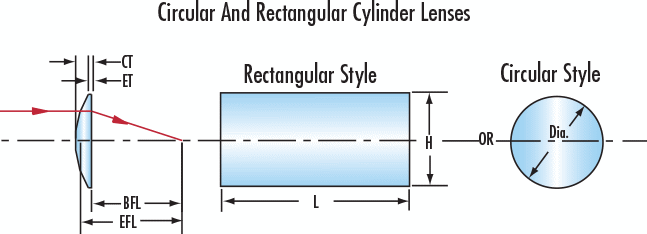
Figure 1: Plano-Convex Circular Cylinder Lens
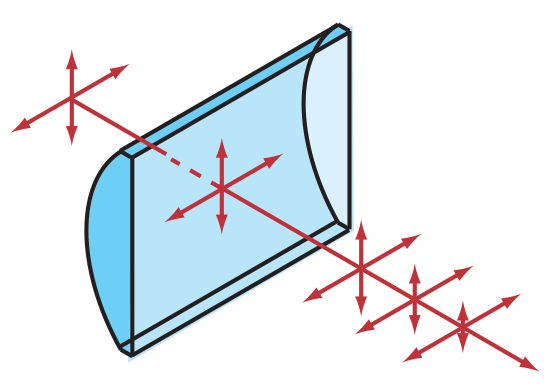
Figure 2: Plano-Convex Rectangular Cylinder Lens
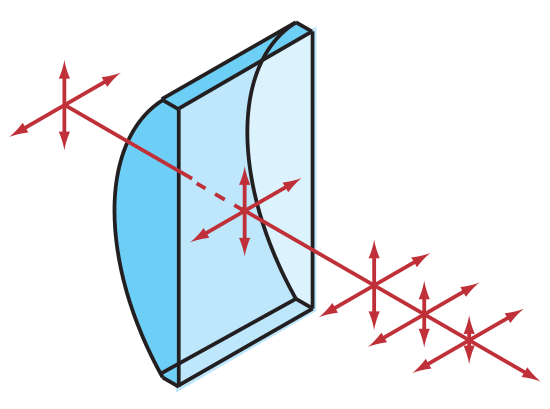
Figure 3: Plano-Convex Oblong Cylinder Lens
Creating a Laser Line Generator
When using a cylinder lens as a laser line generator, it is important to calculate the required Effective Focal Length $ \small{\left( \text{EFL} \right)} $ for the application. To do so, first calculate the fan angle $ \small{ \left( \theta \right)} $ using the needed line length $ \small{\left( x \right)} $ at the given working distance $ \small{\left( L \right)} $ in centimeters:
The fan angle can also be used to determine the line length at a given working distance:
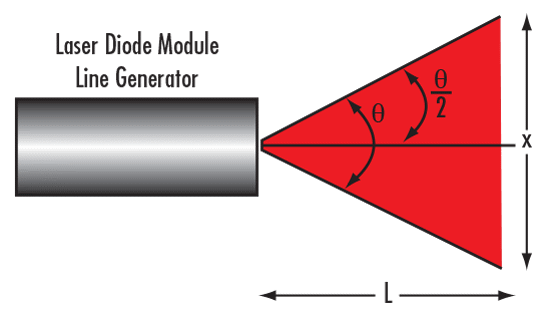
Figure 4: Visual Illustration of Equations 1 – 2 for Creating a Laser Line Generator
The $ \small{\left( \text{EFL} \right)} $can then be calculated using the input beam radius $ \small{ \left( \frac{d}{2} \right) } $ and the following equation:
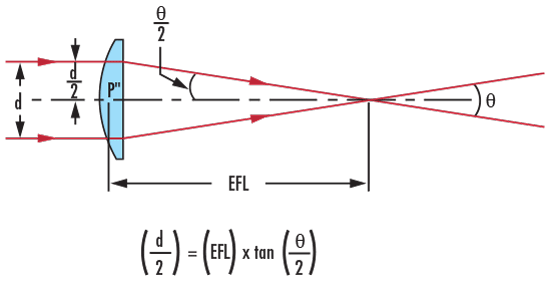
Figure 5: Visual Illustration of Equation 3 for Calculating Effective Focal Length
Creating Circular Beams
Typically, laser diodes emit elliptical-shaped beams that may be unsuitable for applications that require a collimated, circular laser source. Using two cylinder lenses is a common method to circularize an elliptical beam - the first lens magnifies the minor axis of the laser diode, and the second lens collimates the beam. The curved side of the lenses and the minor axis of the laser diode should be oriented so that the minor axis is magnified.
For example, to modify an elliptical beam with a 4.0mm major axis and a 1.0mm minor axis to a circular beam with a 4.0mm diameter, the minor axis needs to be magnified by 4X. The magnification power (Mag) of a two-lens setup can be calculated by dividing the focal length of the second lens $ \small{\left( f_2 \right)} $ by the focal length of the first $ \small{\left( f_1 \right)} $.
One way to achieve the required magnification is to use a 25mm diameter x -25mm EFL PCV Cylinder Lens (#46-196) with a 25mm diameter x 100mm EFL PCX Cylinder Lens (#46-018). Two PCX cylinder lenses can also be used, but add additional length to the system. The use of cylinder lenses also decreases beam divergence, increasing the beam’s collimation, which is ideal for long-distance projection applications. To help in selecting the right cylinder lens for any application, refer to Table 1.
Cylindrical Lens Selection Guide
Ready to purchase a cylindrical lens? Edmund Optics supplies a wide variety of cylinder lenses to choose from. Use our cylindrical lens selection guide below, or visit our cylindrical lenses page to view our full range of lenses.
| Table 1: Cylinder Lens Selection Guide | ||
|---|---|---|
| Type | Wavelength | Ideal Application |
| Fast Axis Collimators | 0.8 – 1.0μm | Collimating high power laser diode bars |
| Illunimation PCX Cylinder Lenses | 0.4 - 1.6μm | Focusing a laser to a line or circularizing a laser beam |
| UV Fused Silica PCX Cylinder Lenses | 0.2 - 2.2μm | Operating in harsh or rugged environments |
| Achromatic Cylinder Lenses | 0.4 - 1.0μm | Creating line profiles of broadband light sources |
| Plastic Hybrid Acylinder Lenses | 0.4 - 1.6μm | Creating line profiles of broadband light sources |
| Illumination PCV Cylinder Lenses | 0.4 - 1.6μm | Beam expansion |
| Cylindrical Microlens Arrays | 0.2 - 2.2μm | Beam homogenization |
Still not sure which type of cylindrical lens would be best for your application, and need some more guidance? Contact us and an expert will help you choose the best cylinder lens for your application.

























or view regional numbers
QUOTE TOOL
enter stock numbers to begin
Copyright 2023 | Edmund Optics, Ltd Unit 1, Opus Avenue, Nether Poppleton, York, YO26 6BL, UK
California Consumer Privacy Acts (CCPA): Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
California Transparency in Supply Chains Act